先来一个最入门的 HDU 1693
哈密顿回路 多回路
Problem Description
Most of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge is a strong hero in the first period of the game. When the game goes to end however, Pudge is not a strong hero any more. So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells. There are several rules Pudge must follow: I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit. II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear. III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
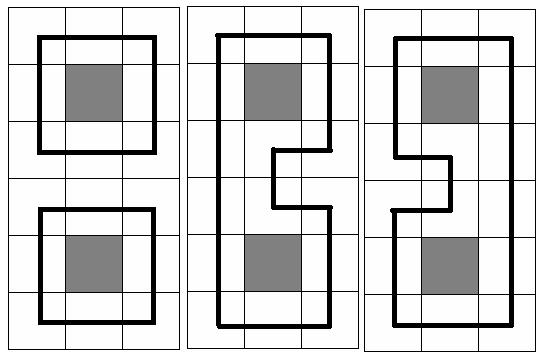
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of the input is the number of the cases. There are no more than 10 cases. For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
Output
For each case, you should print the desired number of ways in one line. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 263 – 1. Use the format in the sample.
Sample Input
2
6 3
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
2 4
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case 1: There are 3 ways to eat the trees.
Case 2: There are 2 ways to eat the trees.
本题就是一道最基础的求回路的题目
因为我们不需要 要求一条回路,所以只需记录是否有插头就可以了
#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>using namespace std;const int Max = (1 << 12) + 10;int n, m;int mp[12][12];long long DP[12][12][Max];
void dp(){ memset(DP, 0, sizeof(DP)); DP[0][m][0] = 1; int bit = 1 << (m + 1); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < (bit >> 1); j++) { DP[i][0][j << 1] = DP[i - 1][m][j]; } for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { for (int k = 0; k < bit; k++) { int x = 1 << (j - 1); int y = 1 << j; if (mp[i][j]) { DP[i][j][k] += DP[i][j - 1][k ^ x ^ y]; if ((k & x) && (k & y)) continue; if (!(k & x) && !(k & y)) continue; DP[i][j][k] += DP[i][j - 1][k]; } else { if (!(k & x) && !(k & y)) DP[i][j][k] = DP[i][j - 1][k]; else DP[i][j][k] = 0; } } } }}int main(){ int t, num = 0; scanf("%d", &t); while (t--) { scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { scanf("%d", &mp[i][j]); } } dp(); printf("Case %d: There are %lld ways to eat the trees.\n", ++num, DP[n][m][0]); } //while(1);}然后是稍微复杂点的
单回路
【题目描述】
Smith在P市的邮政局工作,他每天的工作是从邮局出发,到自己所管辖的所有邮筒取信件,然后带回邮局。 他所管辖的邮筒非常巧地排成了一个m*n的点阵(点阵中的间距都是相等的)。左上角的邮筒恰好在邮局的门口。 Smith是一个非常标新立异的人,他希望每天都能走不同的路线,但是同时,他又不希望路线的长度增加,他想知道他有多少条不同的路线可走。
你的程序需要根据给定的输入,给出符合题意的输出: l 输入包括点阵的m和n的值; l 你需要根据给出的输入,计算出Smith可选的不同路线的总条数;
【输入格式】
输入文件postman.in只有一行。包括两个整数m, n(1 <= m <= 10, 1 <= n <= 20),表示了Smith管辖内的邮筒排成的点阵。
【输出格式】
输出文件只有一行,只有一个整数,表示Smith可选的不同路线的条数。 【样例输入】
2 2 说明:该输入表示,Smith管辖了2*2的一个邮筒点阵。 【样例输出】
2
【提示】
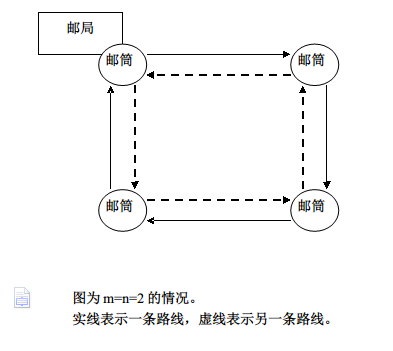
详情请看代码
#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <deque>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int BA = 100000, SIZEN = 10, SIZEM = 20, BASE = 200000;int N, M;int H[BASE];class BigNum /**高精度 */{ public: int n; int s[50]; void operator=(int a) { n = 1; memset(s, 0, sizeof(s)); s[0] = a; } void operator+=(BigNum a) { n = max(n, a.n) + 1; for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { s[i] += a.s[i]; s[i + 1] += s[i] / BA; s[i] %= BA; } while (n > 0 && s[n - 1] == 0) { n--; } } void operator*=(int a) { n++; for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) s[i] *= a; for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { s[i + 1] += s[i] / BA; s[i] %= BA; } while (n > 0 && s[n - 1] == 0) { n--; } } void print() { printf("%d", s[n - 1]); for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) printf("%05d", s[i]); }} ans;
class Pair /**映射表 */{ public: BigNum Sum; LL Id; Pair() {} Pair(LL a, BigNum b) { Id = a; Sum = b; }};deque<Pair> f[2]; /**循环数组 */void read() /**read */{ scanf("%d%d", &N, &M); if (N < M) swap(N, M);}int Get(int x, int j) /**取4进制的操作 */{ x >>= 2 * (j - 1); x &= 3; return x;}int Change(int x, int j, int t) /**把x的第j位改成t */{ int tmp = x >> (2 * (j - 1)); x -= tmp << (j - 1) * 2; tmp >>= 2; x += tmp << 2 * j; x += t << ((j - 1) * 2); return x;}int Find(int x, int j, int dat) /**找与他相连的括号 */{ int now = dat, k = j; while (k >= 1 && k <= M + 1) { k += now; int tmp = Get(x, k); if (tmp == 1) dat++; if (tmp == 2) dat--; if (dat == 0) return k; }}void Push(int k, int Id, BigNum Sum) /**插入hash表 */{ int now = Id % BASE; while (H[now]) /**如果有 */ { if (f[k][H[now]].Id == Id) /**且就是这个状态 */ { f[k][H[now]].Sum += Sum; /**加值,和并答案 */ return; } now++; /**找自己的状态 */ if (now == BASE) now = 0; } H[now] = f[k].size(); /**如果第一次出现 */ f[k].push_back(Pair(Id, Sum));}/** * 1为左括号 * 2为右括号 * 0为无括号 */void DP(){ int k = 0; BigNum p; p = 1; /**初始化状态 */ f[k].push_back(Pair(0, p)); for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= M; j++) { k ^= 1; /**滚动数组 */ f[k].clear(); /**清空本维 */ memset(H, 0, sizeof(H)); /**hash 数组 */ for (int m = 0; m < f[k ^ 1].size(); m++) { int Id = f[k ^ 1][m].Id; /**取状态 */ BigNum date = f[k ^ 1][m].Sum; /**取值 */ int L = Get(Id, j), U = Get(Id, j + 1); /** * L:左面的 ,U: 右面的 */ int tmp; /**分类讨论开始 */ if (!L && !U) /**两个插头都是无插头状态 */ { if (i != N && j != M) /**如果不是最后一个 */ { tmp = Change(Id, j, 1); /**构造一组新的括号 */ tmp = Change(tmp, j + 1, 2); Push(k, tmp, date); /**插入Hash */ } } else if (!L && U) /**左面的没有 */ { if (j != M) /**向右转移 */ Push(k, Id, date); /**延续状态 当j==M事不能向右动*/ if (i != N) /**向下转移 */ { /**将L,U位置的 状态互换 转移*/ tmp = Change(Id, j, U); tmp = Change(tmp, j + 1, 0); Push(k, tmp, date); } } else if (L && !U) /**上面的没有 */ { if (i != N) /**向下 */ Push(k, Id, date); if (j != M) /**向右 */ { /**于上同理 */ tmp = Change(Id, j, 0); tmp = Change(tmp, j + 1, L); Push(k, tmp, date); } } else if (L == 1 && U == 1) /**两个都是左括号 */ { tmp = Change(Id, Find(Id, j + 1, 1), 1); /**将与上面相连的右括号转为左括号 */ tmp = Change(tmp, j, 0); /**这两位都制为无括号 */ tmp = Change(tmp, j + 1, 0); Push(k, tmp, date); } else if (L == 2 && U == 2) /**两个都是右括号 */ { /**与上面对称 */ tmp = Change(Id, Find(Id, j, -1), 2); /**将与左面相连的左括号制为右括号 */ tmp = Change(tmp, j, 0); /**这两位都为无括号 */ tmp = Change(tmp, j + 1, 0); Push(k, tmp, date); } else if (L == 2 && U == 1) /**左插头为右括号 上插头为左括号 */ { /**都制为无 */ tmp = Change(Id, j, 0); tmp = Change(tmp, j + 1, 0); Push(k, tmp, date); } else if (L == 1 && U == 2) { if (i == N && j == M) ans += date; } } } for (int km = 0; km < f[k].size(); km++) /**提前换行准备为下一行使用 */ f[k][km].Id <<= 2; } ans *= 2; ans.print();}int main(){ //freopen("postman.in", "r", stdin); //freopen("postman.out", "w", stdout); read(); if (M == 1) { printf("1"); return 0; } DP(); return 0;}